Step 2: Inbound Template Request Body (JSON Body) (Old Interface)
Request Body Page (JSON Builder)
If the selected Method is other than GET and you selected JSON as the request body format, you will be presented with this page at step 2. This is where you build the expected request JSON body.
NOTE: Just as the callout template will not let you change the Main Object once in the JSON Builder, inbound templates function the same. Once you start mapping fields in the JSON Builder, you CANNOT change the Main Object. If you want to change either of these, you need to remove all values set in the JSON Builder. Then you have the option to update the Main Object. This is by design as the values set in JSON are dependent on the Main Object selected.
About JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write. It is also easy for machines to parse and generate.
JSON is built on two structures:
- A collection of name/value pairs.
- An ordered list of values.
An object is an unordered set of name/value pairs. An object begins with { (left brace) and ends with } (right brace). Each name is followed by : (colon) and the name/value pairs are separated by , (comma). A value can be a string in double quotes, or a number, or true or false or null, or an object or an array. Exmaple: { “name” : “Maria”, “age” : 30 }
An array is an ordered collection of values. An array begins with [ (left bracket) and ends with ] (right bracket). Values are separated by , (comma). Example: [ “orange”, “apple”, “cherry” ]
These structures can be nested. Example: { “name” : { “first” : “John”, “last” : “Doe” } , “email” : “john@example.com”, “children_age” : [ 12, 8, 3 ] }
More about JSON here: https://www.w3resource.com/JSON/introduction.php
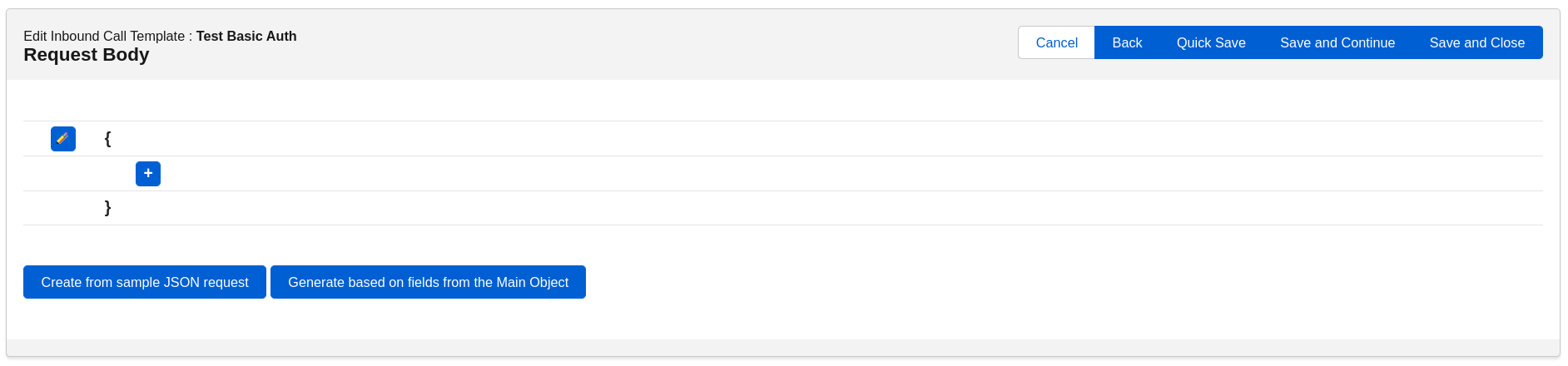
Request Body
Just as you do in the callout template, here is where you will build the JSON body structure. To get started, select the ‘+’ icon as displayed below:
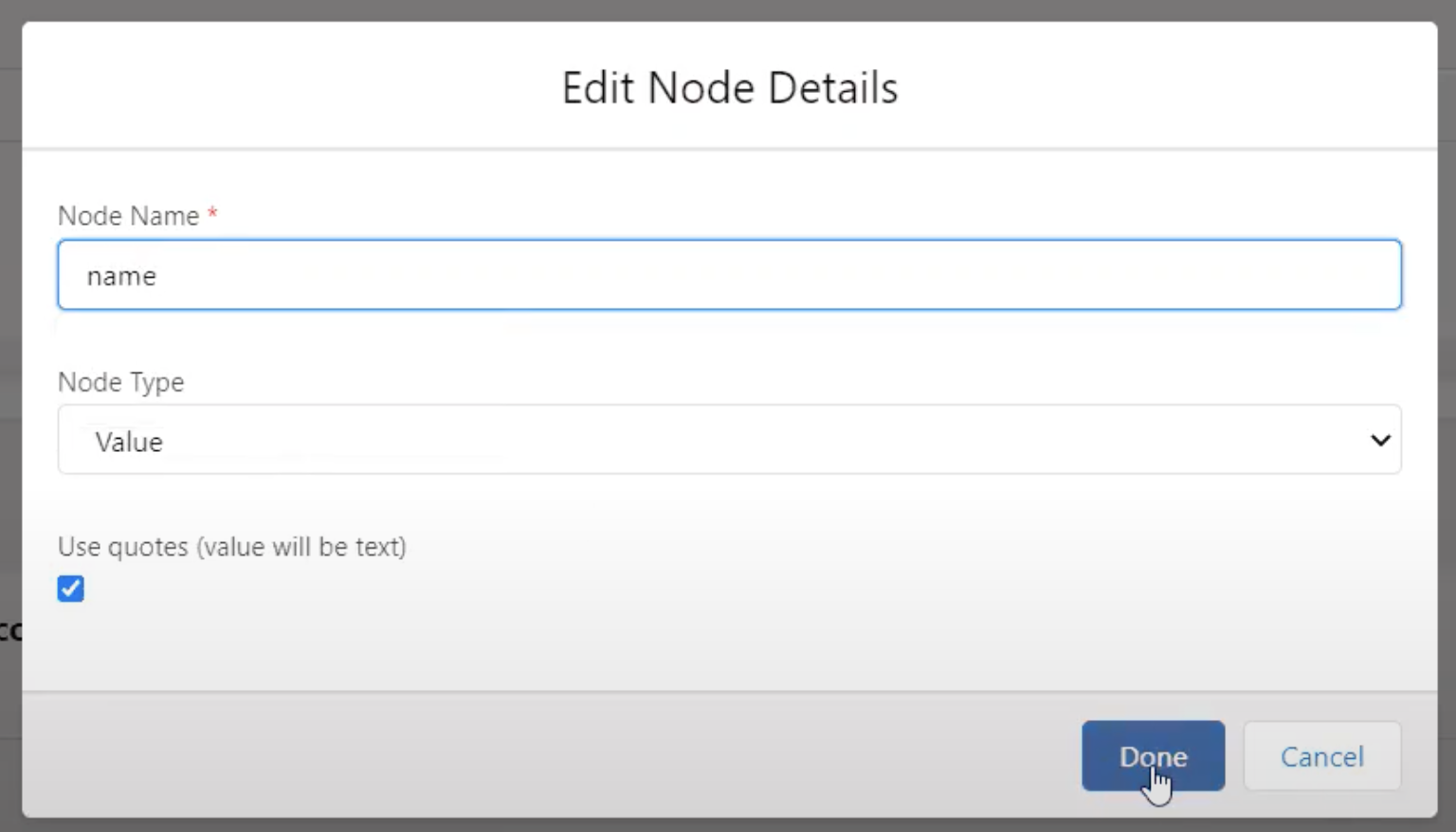
In the builder, first we need to give our key, or Node Name, a name to define the value. Then we have options to select either Object, List, Value or Array in the Node Type. Our Main Object in this example is Account. Let’s say we want to grab the Account Name. We start by giving the Node Name something that easily tells us what we are receiving from the external system. So, in this case it makes sense to call it ‘Name.’
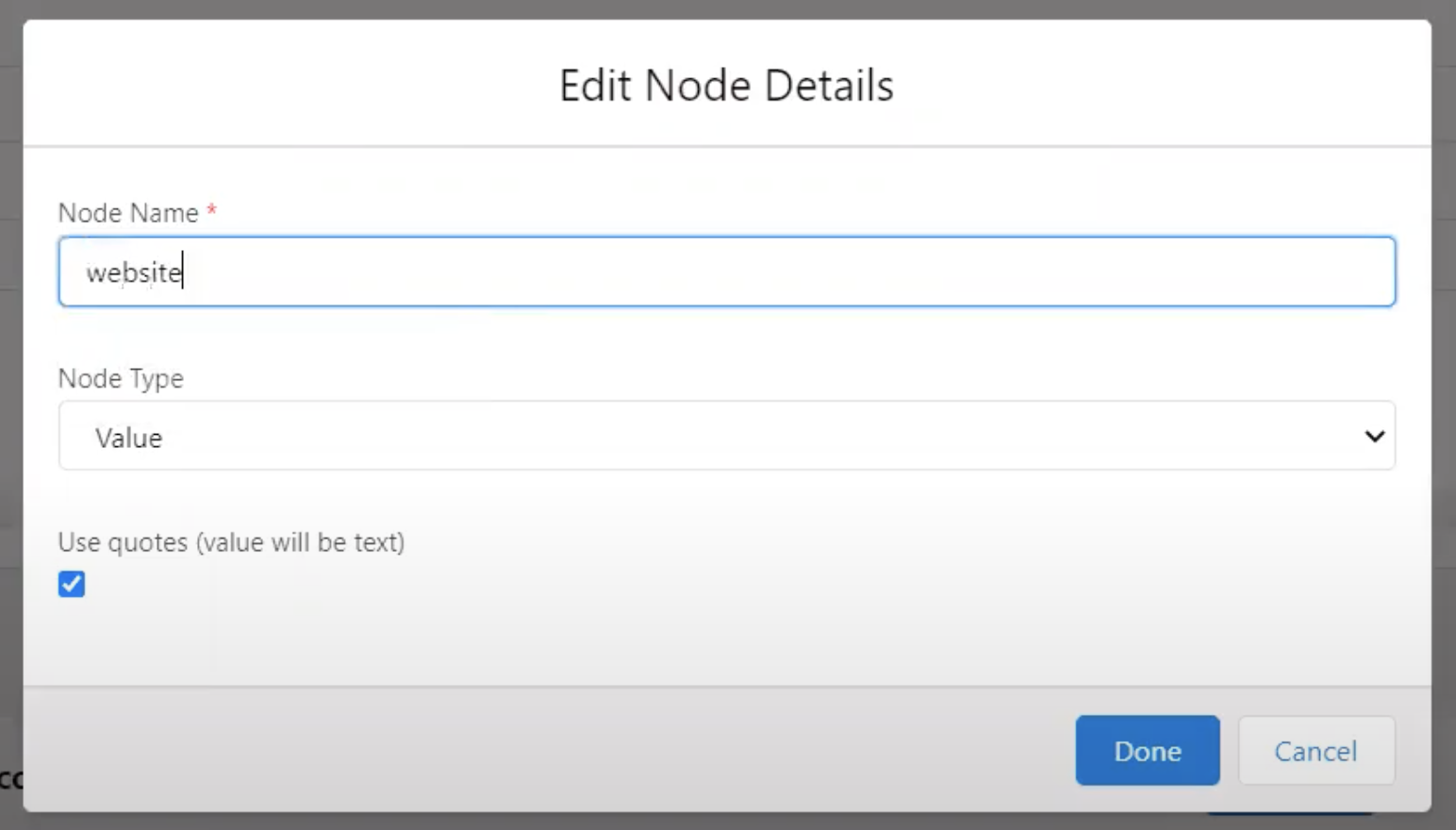
Our Node Type will remain as value because we are looking to receive the VALUE, or specific Account Name, from the external system to be created or updated in Salesforce. Let’s say we also want to capture the website. We will create a second node for website with a Node Type of ‘Value.’
Create from sample JSON request
If you have a JSON Sample from the API documentation from the app or platform being implemented, you can create your Request Body quickly by utilizing the ‘Create from sample JSON request’ button. You will see the Return Body generated for you. As mentioned, you can also do this manually by creating your Node Name and Node Type, but again, no values or fields will be mapped.
Generate based on fields from Main Object
If you expect the incoming request body to contain field names from the main object, you can use the “Generate based on fields from Main Object” button to generate the expected request body.